Integrating Vector Search in E-commerce Platforms with Upstash Vector
Imagine an online fashion retailer that wants to give its visitors the best possible shopping experience. Now... how do they do that? As numerous studies have shown over the last few years and even decades, a key part of the answer is relevant, personalised product recommendations.
In this article, we'll use vector embeddings to store a representation of all of our inventory (products) to create personalised product recommendations in real-time. Best of all: We can base these recommendations not only on product text (i.e. title and/or description), but also, as we'll see later, on product images! The better the recommendations we make, the better the shopping experience for the visitor.
So in this guide, you'll learn how to create vector embeddings of images and text. Along the way, we'll use modern and fun-to-use tools like the Astro framework (which is very fast). You'll also learn how to search for similar products based on user input - something you'll see on popular e-commerce sites in the "you might also like" section. Let's get started!
Prerequisites
You will need the following:
- Node.js 18 or later
- Python 3.6+ or later
- An Upstash account
Tech Stack
Following technologies are used in this guide:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Upstash | Serverless database platform. You're going to use Upstash Vector for storing vector embeddings and metadata. |
| FastAPI | A high performance framework to build APIs with Python 3.8+. |
| Astro | Framework for building fast, modern websites with serverless backend support. |
| TailwindCSS | CSS framework for building custom designs. |
Create an Upstash Vector Index
Once you have created an Upstash account and are logged in, go to the Vector tab and click on Create Index to start creating a vector index.
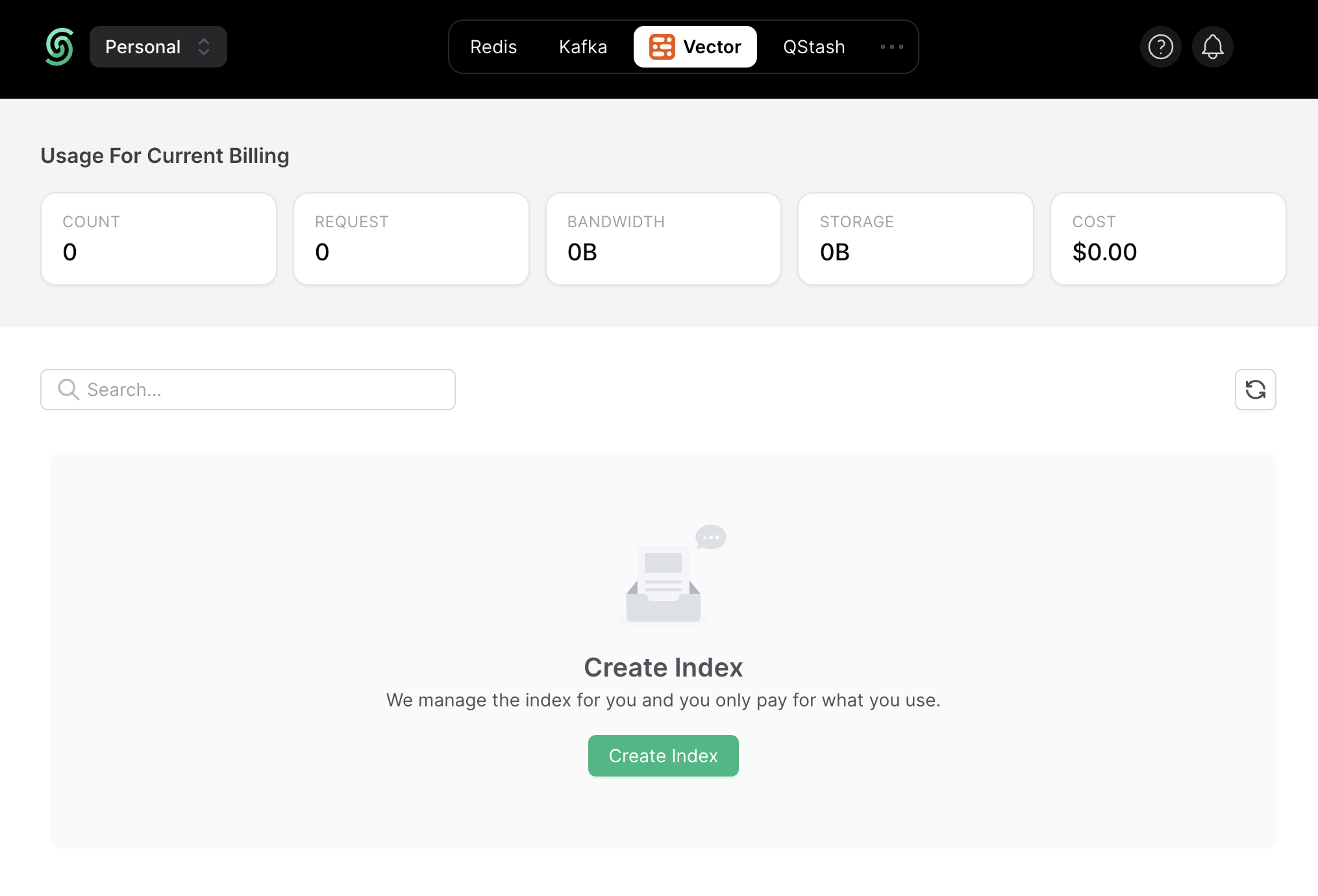
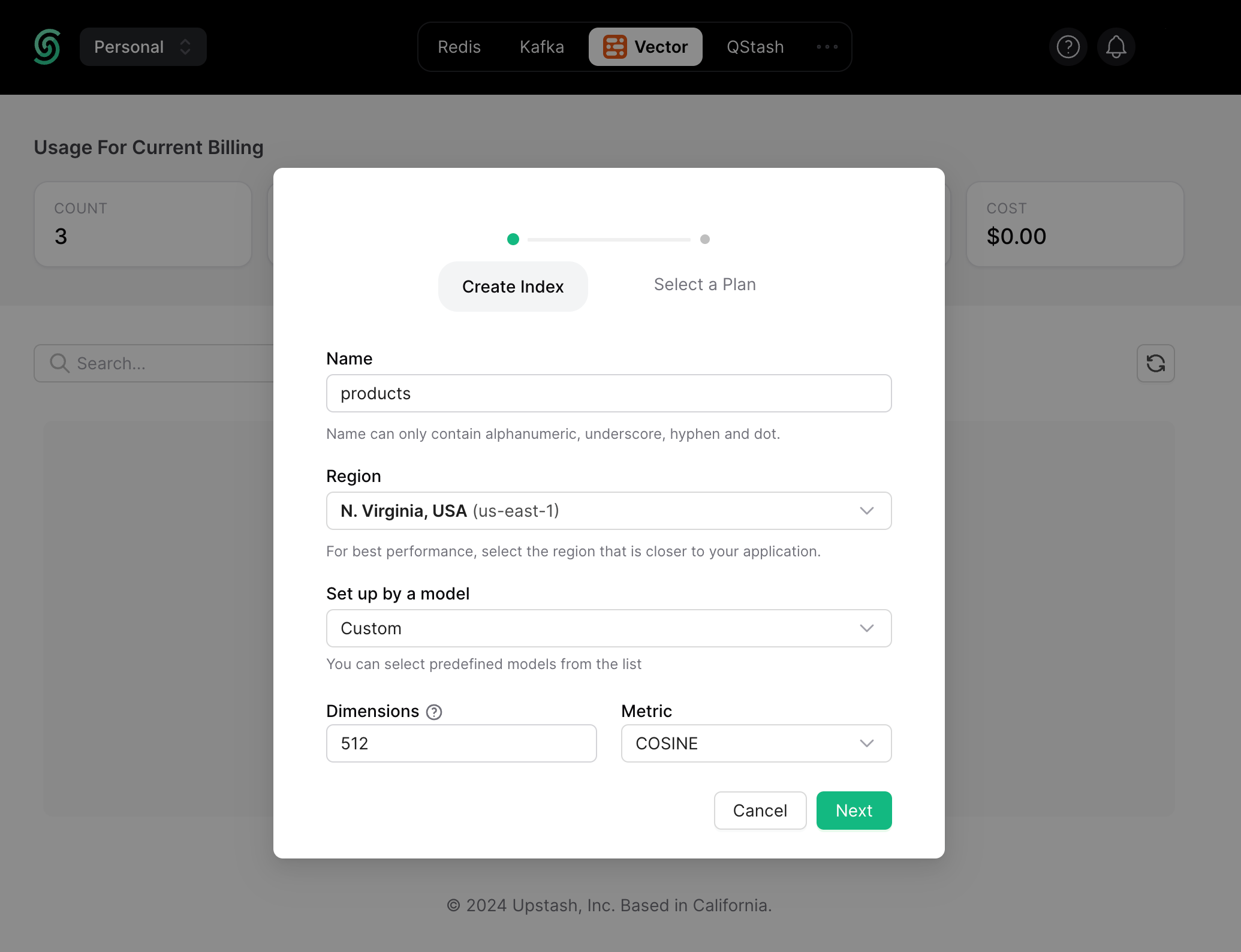
Enter the index name of your choice (say, products) and set the vector dimensions to be of 512.
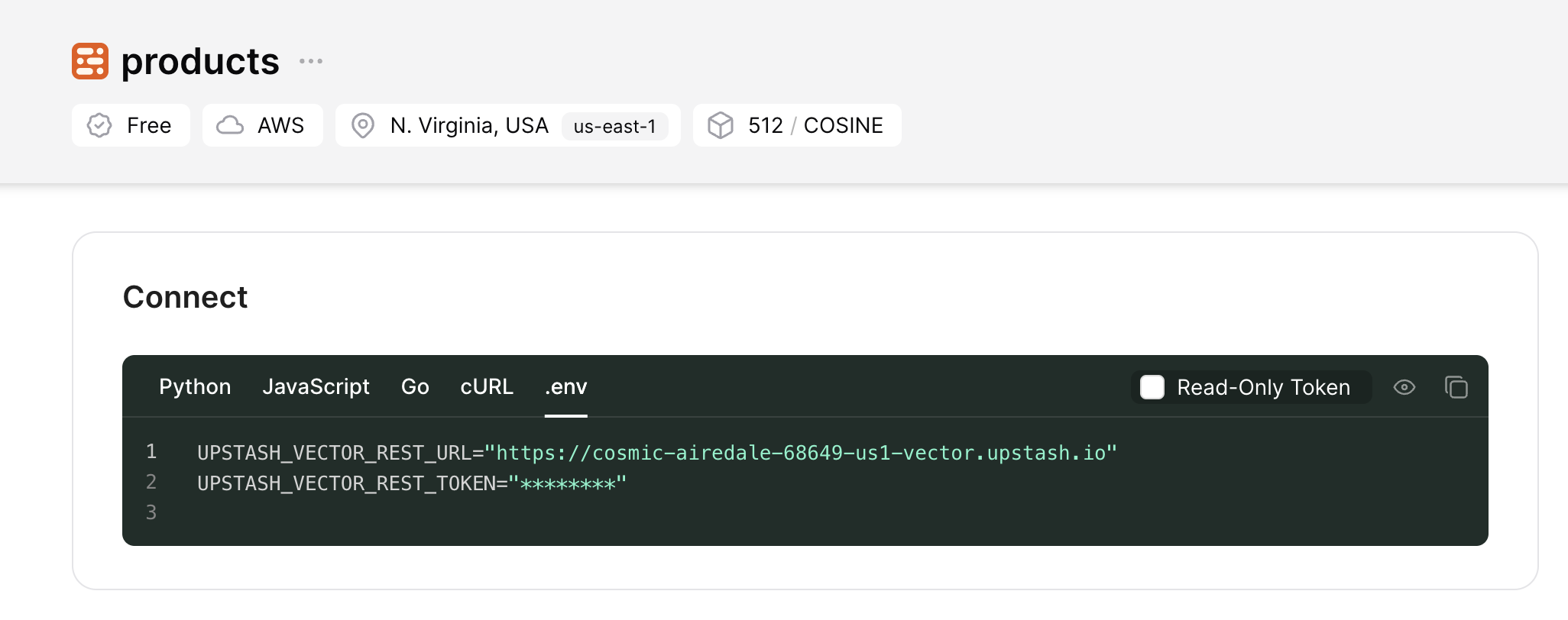
Now, scroll down till the Connect section, and click the .env button. Copy the contents, and save it somewhere safe to be used further in your application.
Create a new FastAPI application
Let’s get started by creating a new FastAPI project. Open your terminal and run the following commands:
# Create and move to the new directory
mkdir ecommerce-vector-search-server
cd ecommerce-vector-search-server
# Create a main.py file
touch main.py# Create and move to the new directory
mkdir ecommerce-vector-search-server
cd ecommerce-vector-search-server
# Create a main.py file
touch main.pyThe commands above create a directory named ecommerce-vector-search-server with an empty main.py file in it.
Once you have cloned the repo, create an .env file. You are going to add the secret keys obtained in the sections above.
The .env file should contain the following keys:
# .env
# Upstash Vector Keys
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL="https://...-us1-vector.upstash.io"
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN="...="# .env
# Upstash Vector Keys
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL="https://...-us1-vector.upstash.io"
UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN="...="Next, in your first terminal window, run the command below to install the necessary libraries for building the application:
pip install fastapi "uvicorn[standard]"
pip install upstash_vector
pip install python_dotenv torch pillow transformers numpypip install fastapi "uvicorn[standard]"
pip install upstash_vector
pip install python_dotenv torch pillow transformers numpyThe above command installs the following packages:
fastapi: A modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints.uvicorn[standard]: A lightning-fast ASGI server. The[standard]part indicates that you're installing Uvicorn with the standard set of dependencies.upstash_vector: A serverless Vector SDK (python) from Upstash.python_dotenv: A package to manage environment variables in a .env file.torch: A popular open-source machine learning library for Python, PyTorch.pillow: The Python Imaging Library (PIL) for opening many different image file formats.numpy: A package for scientific computing with Python.transformers: A library (by Hugging Face) for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, providing implementations of state-of-the-art pre-trained models such as BERT, GPT, and others.
Once they are installed, append the following to the main.py file:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
# Initialize FastAPI App
app = FastAPI()
# Add CORS middleware
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
# Initialize FastAPI App
app = FastAPI()
# Add CORS middleware
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)Now, let's move on to creating a function to generate vector embeddings from text input(s).
Generate Text Embeddings using CLIPTextModel
Let's define a function to transform text into embeddings using the CLIPText model. Append the following code to main.py file:
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPTextModel
# Initialize the CLIP processor
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Initialize the CLIPTextModel
text_model = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Function to generate vector embeddings from text
def getTextEmbeddings(text):
pooled_output = []
inputs = processor(text, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
with torch.no_grad():
text_features = text_model(**inputs)
pooled_output = text_features.pooler_output
return pooled_output[0]import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPTextModel
# Initialize the CLIP processor
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Initialize the CLIPTextModel
text_model = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Function to generate vector embeddings from text
def getTextEmbeddings(text):
pooled_output = []
inputs = processor(text, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
with torch.no_grad():
text_features = text_model(**inputs)
pooled_output = text_features.pooler_output
return pooled_output[0]The code above does the following:
- Initializes CLIPProcessor, which preprocesses text inputs for the CLIP model. It is using the openai/clip-vit-base-patch32 variant.
- Initializes CLIPTextModel, which represents the text-processing component of the CLIP model, using the same variant as the processor.
- Creates a function named
getTextEmbeddingsthat takes a text input, preprocesses it using the initialized processor, feeds it into the CLIPTextModel, and returns the pooled output, which represents the vector embedding of the text.
Let's move on to generating vector embeddings of images with CLIP model.
Generate Image Embeddings using CLIPModel
Let's define a function (along with some helper functions) to fetch, and transform images into embeddings using the CLIP model. Append the following code to main.py file:
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel, CLIPTextModel
# Initialize the CLIPModel
image_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Image preprocesser
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# Function to fetch remote image
def getImage(url):
res = requests.get(url, stream=True)
return Image.open(res.raw)
# Function to generate vector embeddings from images
def getImageEmbeddings(image):
image = preprocess(image)
image = image.unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
features = image_model.get_image_features(pixel_values=image)
embedding = features.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
return embedding.astype(np.float32)import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel, CLIPTextModel
# Initialize the CLIPModel
image_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
# Image preprocesser
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# Function to fetch remote image
def getImage(url):
res = requests.get(url, stream=True)
return Image.open(res.raw)
# Function to generate vector embeddings from images
def getImageEmbeddings(image):
image = preprocess(image)
image = image.unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
features = image_model.get_image_features(pixel_values=image)
embedding = features.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
return embedding.astype(np.float32)The code above does the following:
- Initializes CLIPModel, which represents the image-processing component of the CLIP model, using the openai/clip-vit-base-patch32 variant.
- Defines a series of transformations using
torchvision.transformsto preprocess the input image, including resizing, conversion to tensor, and normalization. - Creates a
getImagefunction that takes a URL as input, fetches the corresponding image from the internet, and returns it as a PIL image object. - Creates a
getImageEmbeddingsfunction that preprocesses the input image using the defined transformations, feeds it into the CLIPModel to obtain image features, and returns the embedding as a numpy array.
Create Upstash Vector Client
Using upstash_vector library, you are able to create a connectionless client in your FastAPI application that allows you to store, delete, and query vector embeddings from an Upstash Vector index. Append the following code to main.py file:
import upstash_vector as uv
from dotenv import dotenv_values
# Load environment variables
env_config = dotenv_values(".env")
# Initialize Upstash Vector Index
index = uv.Index(
url=env_config["UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL"],
token=env_config["UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN"]
)import upstash_vector as uv
from dotenv import dotenv_values
# Load environment variables
env_config = dotenv_values(".env")
# Initialize Upstash Vector Index
index = uv.Index(
url=env_config["UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_URL"],
token=env_config["UPSTASH_VECTOR_REST_TOKEN"]
)With that done, let's use both the vector embeddings generator functions in FastAPI endpoints.
Dynamically update Upstash Vector Index with new products
With increasing inventory, e-commerce are ever growing. Hence, to visualize things like in real-time, you are going to create an API that would dynamically create embeddings of the products from it's attributes such as image, title and description and store them in the Upstash Vector index. This helps keeps the data up-to-date, resulting in accurate responses to user searches. Append the following code to main.py file:
@app.post("/api/add")
async def add(request: Request):
# Load JSON data from the request body
request_body = await request.json()
products = request_body['products']
# Loop over each product
for product in products:
embedding = []
# If the product has an image field
if product["image"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the image of the product
image = getImage(product["image"])
embedding = getImageEmbeddings(image)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])
if product["title"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the title of the product
text = product["title"]
embedding = getTextEmbeddings(text)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])
if product["description"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the description of the product
description = product["description"]
embedding = getTextEmbeddings(description)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])@app.post("/api/add")
async def add(request: Request):
# Load JSON data from the request body
request_body = await request.json()
products = request_body['products']
# Loop over each product
for product in products:
embedding = []
# If the product has an image field
if product["image"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the image of the product
image = getImage(product["image"])
embedding = getImageEmbeddings(image)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])
if product["title"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the title of the product
text = product["title"]
embedding = getTextEmbeddings(text)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])
if product["description"]:
# Generate vector embeddings of the description of the product
description = product["description"]
embedding = getTextEmbeddings(description)
# Insert the vector embeddings along with metadata into Upstash Vector
index.upsert(vectors = [(random.random(), embedding.tolist(), product)])The code above does the following:
- The endpoint parses the request body to extract product data.
- For each product, it checks if it has an image, title, or description field.
- If present, it generates vector embeddings using
getImageEmbeddingsorgetTextEmbeddingsfunctions. - It then inserts these embeddings into Upstash Vector index along with metadata using the upsert method, ensuring that the index is dynamically updated with new product information.
Dynamically search from Upstash Vector Index for similar products
For the UI to render rich product information responses to user queries, you are going to return the relevant product information by creating an endpoint it can talk to. Such an endpoint would be responsible to search for the relevant products based on the user prompt, including link to images. Append the following code to main.py file:
@app.post("/api/chat")
async def chat(request: Request):
# Load JSON data from the request body
request_body = await request.json()
messages = request_body['messages']
# Get the latest user message
user_input = messages[-1]['content']
query_embedding = []
# If image URL was passed in the latest user query and get it's vector embeddings
if "https://" in user_input:
query_embedding = getImageEmbeddings(getImage(user_input))
# Else assume text and get it's vector embeddings
else:
query_embedding = getTextEmbeddings(user_input)
# Return the top 3 relevant vectors along with their metadata
output = index.query(vector=query_embedding.tolist(), top_k=3, include_metadata=True)
return [item for item in output if item.score > 0.8]@app.post("/api/chat")
async def chat(request: Request):
# Load JSON data from the request body
request_body = await request.json()
messages = request_body['messages']
# Get the latest user message
user_input = messages[-1]['content']
query_embedding = []
# If image URL was passed in the latest user query and get it's vector embeddings
if "https://" in user_input:
query_embedding = getImageEmbeddings(getImage(user_input))
# Else assume text and get it's vector embeddings
else:
query_embedding = getTextEmbeddings(user_input)
# Return the top 3 relevant vectors along with their metadata
output = index.query(vector=query_embedding.tolist(), top_k=3, include_metadata=True)
return [item for item in output if item.score > 0.8]The code above does the following:
- The endpoint parses the request body to extract user messages.
- It retrieves the latest user input from the messages.
- If the input contains an image URL, it generates embeddings using
getImageEmbeddings; otherwise, it usesgetTextEmbeddingsfor text input. - The generated embeddings are used to query the Upstash Vector index with the query method, specifying to retrieve the top 3 relevant vectors along with their metadata.
- Finally, it filters and returns results with a similarity score higher than 0.8, ensuring relevant product recommendations are provided to the user.
Run the FastAPI Application (Locally)
Execute the following command in another terminal window to build and preview your FastAPI application:
uvicorn main:app --reloaduvicorn main:app --reloadThe app should be running on localhost:8000.
Now, let's move on to creating the user interface for users to interact with.
Create a new Astro application
Let’s get started by creating a new Astro project. Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm create astro@latest ecommerce-vector-search-uinpm create astro@latest ecommerce-vector-search-uinpm create astro is the recommended way to scaffold an Astro project quickly.
When prompted, choose the following:
Emptywhen prompted on how to start the new project.Yeswhen prompted whether to write Typescript.Strictwhen prompted how strict Typescript should be.Yeswhen prompted to whether install dependencies.Yeswhen prompted to whether initialize a git repository.
Once that’s done, you can move into the project directory and start the app:
cd ecommerce-vector-search-ui
npm run devcd ecommerce-vector-search-ui
npm run devThe app should be running on localhost:4321. Let's close the development server as we move on to integrate TailwindCSS into the application.
Add Tailwind CSS to the application
For styling the app, you will be using Tailwind CSS. Install and set up Tailwind CSS at the root of our project's directory by running:
npx astro add tailwindnpx astro add tailwindWhen prompted, choose:
Yeswhen prompted to install the Tailwind dependencies.Yeswhen prompted to generate a minimaltailwind.config.mjsfile.Yeswhen prompted to make changes to Astro configuration file.
With choices as above, the command finishes integrating TailwindCSS into your Astro project. It installed the following dependency:
tailwindcss: TailwindCSS as a package to scan your project files to generate corresponding styles.@astrojs/tailwind: The adapter that brings Tailwind's utility CSS classes to every.astrofile and framework component in your project.
To create reactive interfaces quickly, let’s move onto integrating React in your Astro application.
Integrate React in your Astro project
To prototype the reactive user interface quickly, you are gonna use React as the library with Astro. In your terminal window, execute the following command:
npx astro add reactnpx astro add reactnpx allows us to execute npm packages binaries without having to first install it globally.
When prompted, choose the following:
Yeswhen prompted whether to install the React dependencies.Yeswhen prompted whether to make changes to Astro configuration file.Yeswhen prompted whether to make changes totsconfig.jsonfile.
To create conversation user interface with product recommendations easily in React, let’s move on to installing an AI SDK in your Astro application.
Install Vercel AI SDK
In your terminal window, run the command below to install the necessary library for building the conversation user interface:
npm install ainpm install aiThe above command installs the following:
ailibrary to build AI-powered streaming text and chat UIs.
Build Chat (with Product Recommendations) User Interface
To display product recommendations in a visually appealing format, including product images, titles, and descriptions, create a Recommend.jsx file inside the src directory with the following code:
// File: src/Recommend.jsx
import { useChat } from "ai/react";
export default function () {
const { messages, handleSubmit, input, handleInputChange } = useChat({
api: "http://localhost:8000/api/chat",
});
return (
<form
onSubmit={handleSubmit}
className="mt-12 flex w-full max-w-[300px] flex-col"
>
<input
id="input"
name="prompt"
value={input}
autoComplete="off"
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Describe the product you're looking for."
className="mt-3 min-w-[300px] rounded border px-2 py-1 outline-none focus:border-black"
/>
<button
type="submit"
className="mt-3 max-w-max rounded border px-3 py-1 outline-none hover:bg-black hover:text-white"
>
Find →
</button>
{messages.map((message, i) =>
message.role === "assistant" ? (
<div className="mt-3 border-t pt-3 flex flex-col">
{
JSON.parse(message.content).map((product, _) => (
<div key={product.metadata.image} className="mt-3 flex flex-col">
<img alt={product.metadata.title} src={product.metadata.image} />
<span>{product.metadata.title}</span>
<span>{product.metadata.description}</span>
</div>
))}
</div>
) : (
<div className="mt-3 border-t pt-3" key={i}>
{message.content}
</div>
)
)}
</form>
);
}// File: src/Recommend.jsx
import { useChat } from "ai/react";
export default function () {
const { messages, handleSubmit, input, handleInputChange } = useChat({
api: "http://localhost:8000/api/chat",
});
return (
<form
onSubmit={handleSubmit}
className="mt-12 flex w-full max-w-[300px] flex-col"
>
<input
id="input"
name="prompt"
value={input}
autoComplete="off"
onChange={handleInputChange}
placeholder="Describe the product you're looking for."
className="mt-3 min-w-[300px] rounded border px-2 py-1 outline-none focus:border-black"
/>
<button
type="submit"
className="mt-3 max-w-max rounded border px-3 py-1 outline-none hover:bg-black hover:text-white"
>
Find →
</button>
{messages.map((message, i) =>
message.role === "assistant" ? (
<div className="mt-3 border-t pt-3 flex flex-col">
{
JSON.parse(message.content).map((product, _) => (
<div key={product.metadata.image} className="mt-3 flex flex-col">
<img alt={product.metadata.title} src={product.metadata.image} />
<span>{product.metadata.title}</span>
<span>{product.metadata.description}</span>
</div>
))}
</div>
) : (
<div className="mt-3 border-t pt-3" key={i}>
{message.content}
</div>
)
)}
</form>
);
}The code above does the following:
- Utilizes the
useChathook to manage chat functionality. - Renders an input field for the user to describe the product they're looking for and a button to submit the query.
- Upon submission, it sends the user input to the specified API endpoint (http://localhost:8000/api/chat).
- Renders the messages received from the API, displaying product recommendations returned by the server.
- Product recommendations are displayed as images along with their titles and descriptions.
To use this Recommend component on the index route of your Astro application, make the following changes in src/pages/index.astro file:
---
+ import Recommend from '../Recommend'
---
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/favicon.svg" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<meta name="generator" content={Astro.generator} />
<title>Astro</title>
</head>
<body class="flex w-screen flex-col items-center">
- <h1>Astro</h1>
+ <Recommend client:load />
</body>
</html>---
+ import Recommend from '../Recommend'
---
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/favicon.svg" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<meta name="generator" content={Astro.generator} />
<title>Astro</title>
</head>
<body class="flex w-screen flex-col items-center">
- <h1>Astro</h1>
+ <Recommend client:load />
</body>
</html>The changes above do the following:
- Imports the Recommend component.
- Uses Astro's client:load directive to hydrate it immediately as it's loaded.
Test the Astro Application (Locally)
Execute the following command in another terminal window to build and preview your Astro application:
npm run build && npm run previewnpm run build && npm run previewThe app should be running on localhost:4321.
That was a lot of learning! You’re all done now ✨
More Information
For more detailed insights, explore the references cited in this post.
Conclusion
In this guide, you have learned how to enhance user experience by dynamically generating product recommendations based on what they are looking for. With Upstash Vector, you get the ability to store vectors in an index, perform top-K vector search queries and create relevant product recommendations for each user search, all within few lines of code.
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to me on GitHub.
